Imagine building a bridge to connect two cities, but leaving a giant hole in the middle. Traffic stops, people turn around, and the map gets marked as "Do Not Travel."
This is exactly what a Broken Internal Link (404 Error) does to your website.
In traditional SEO, broken links were annoying because they wasted "link juice." But in 2026, with the rise of AI Search and Answer Engines, broken links are catastrophic. They are dead ends that stop AI crawlers (like GoogleOther and GPTBot) from indexing your content.
If an AI bot cannot crawl a page, it cannot read it. If it cannot read it, it cannot cite it in an AI Overview.
This guide explains why "Link Rot" is destroying your potential for AI traffic and how to find and fix every broken link on your site in under 5 minutes.
Why AI Bots Hate Broken Links (The "Trust" Factor)
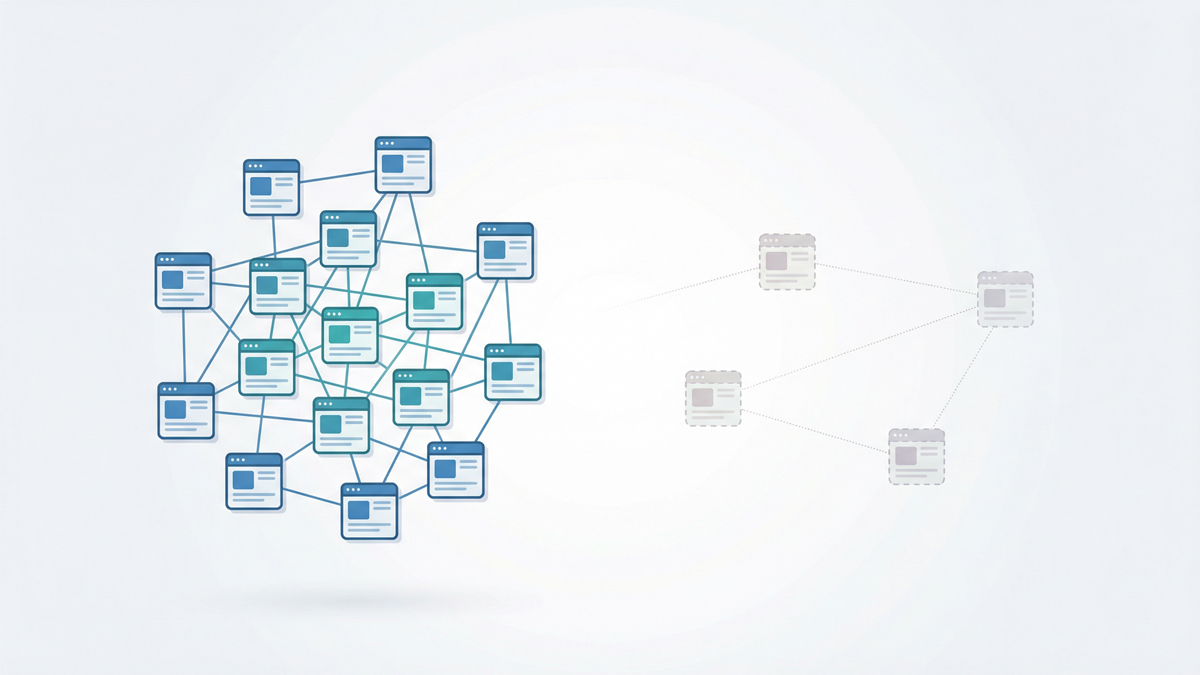
Search engines have evolved. They are no longer just indexing keywords; they are building Trust Maps.
1. The "Crawl Budget" Waste
AI crawlers are expensive to run. Google and OpenAI have limited resources (Crawl Budget) to scan the web.
-
The Scenario: A bot lands on your site and hits 5 broken links in a row.
-
The Consequence: The bot decides your site is "low maintenance" and leaves before indexing your new, high-quality articles. You effectively slammed the door in the AI's face.
2. Breaking the Knowledge Graph
Internal links tell AI how concepts are related.
-
Link: "SEO Tools" $\rightarrow$ "Internal Link Checker."
-
If that link returns a 404 Error, the semantic connection is severed. The AI fails to associate your brand with the "Internal Link Checker" entity because the path is broken.
3. The "Pogo-Sticking" Signal (UX)
Google uses User Experience signals to rank pages. If a user clicks an internal link, sees a "Page Not Found" error, and immediately hits the Back Button, this is called "Pogo-sticking."
-
The Signal: It tells Google's RankBrain algorithm: "This page is broken/low quality."
-
The Result: Your rankings drop, not just for the broken page, but for the linking page too.
What Causes "Link Rot"?
Websites are living things; they decay over time. Even if you are careful, broken links happen due to:
-
URL Changes: You updated a blog post slug (e.g., from /blog/2023-tips to /blog/2026-tips) but forgot to update the old links pointing to it.
-
Deleted Content: You removed an irrelevant product or service page, but 50 blog posts still link to it.
-
Typos: You manually typed a link as your-site.com/servcies instead of /services.
How to Find Broken Internal Links (Free & Fast)
You cannot check every link manually-it's impossible. You need a crawler that simulates a bot.
The Old Way: Buying expensive software or installing heavy desktop apps.
The New Way: Cloud-based, instant analysis.
Step-by-Step Audit:
-
Open the Tool: Go to the SEO Shouts Internal Link Checker.
-
Run a Crawl: Enter your homepage URL. The tool will scan up to 500 pages of your site architecture.
-
Check Status Codes: Look at the "Status" column in the results table.
-
200: OK (Healthy).
-
301: Redirect (Passable, but not ideal).
-
404: Not Found (Critical Error).
-
5xx: Server Error (Urgent Hosting Issue).
-
-
Export & Attack: Download the list of 404s. These are your priority targets.
How to Fix Broken Links: The 3 Strategies
Once you have your list of 404s from the SEO Shouts Tool, you have three options. Choose wisely based on the context.
Strategy 1: The Content Update (Best for SEO)
-
Scenario: You linked to an old page that is deleted, but you have a new relevant page.
-
The Fix: Go to the source page and edit the HTML. Replace the dead link with the direct link to the new page.
-
Why: This saves "latency." It's faster for the user than a redirect and preserves 100% of the link equity.
Strategy 2: The 301 Redirect (The Safety Net)
-
Scenario: You moved a URL (e.g., changed a permalink) and thousands of internal/external links are broken.
-
The Fix: Set up a 301 Redirect at the server level (or use a plugin) from the Old URL $\rightarrow$ New URL.
-
Why: It automatically forwards users and bots. However, try to avoid "Redirect Chains" (Page A $\rightarrow$ Page B $\rightarrow$ Page C) as they dilute authority.
Strategy 3: The Removal (The Pruning)
-
Scenario: You linked to a resource that no longer exists, and you have no replacement.
-
The Fix: Simply remove the hyperlink. Leave the text if it still makes sense, or rewrite the sentence.
-
Why: It stops the bleeding. A text mention is better than a broken link.
Pro Tip: Don't Ignore "Soft 404s"
Sometimes a page looks like a 404 error (it says "Page Not Found"), but the server sends a "200 OK" code. This confuses Google.
-
Detection: If our tool shows a page as "200 OK" but it looks empty, check your specific CMS settings. Ensure your error pages actually send a 404 header response.
Maintenance: The Quarterly "Link Hygiene" Check
Broken links are inevitable. You should schedule a "Link Hygiene" audit once every quarter.
-
Run the SEO Shouts Crawler.
-
Fix the top 10 worst offenders (pages with the most broken links).
-
Check for "Orphan Pages" while you are there (pages that lost their only link).
Conclusion: Keep the Bridges Open
In the AI era, your website is an ecosystem of information. Internal links are the pathways that allow knowledge to flow. If those pathways are broken, the ecosystem dies.
Don't let a few typos or deleted pages sabotage your rankings.
Is your site full of dead ends?
Find every broken link on your site in seconds (Free).